Essential Nutritional Support for Male Well-being: A Comprehensive Guide to Men's Vitamins and Dietary Supplements
Understanding Essential Nutrients
Nutrition forms the foundation of overall health and well-being. Essential nutrients play vital roles in maintaining energy levels, supporting immune function, and promoting general vitality. Whether through balanced dietary choices or supplementation, understanding the role of vitamins, minerals, and other beneficial compounds can help individuals make informed decisions about their nutritional needs.
Key Vitamins for Male Health
- Vitamin D3: Supports immune function and contributes to normal bone maintenance. Often obtained from sunlight exposure or dietary sources like fatty fish.
- Vitamin B12: Essential for energy production and normal nervous system function. Important for red blood cell formation and DNA synthesis.
- Vitamin C: Supports immune system function and acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from oxidative stress. Found abundantly in citrus fruits and vegetables.
- Vitamin E: Works as an antioxidant to protect cells and supports cardiovascular health through normal blood circulation.
- Folate (B9): Contributes to normal amino acid synthesis and supports healthy cellular function.

Minerals and Their Role
Minerals are inorganic compounds that support numerous physiological processes. Zinc plays an important role in immune system support and normal carbohydrate metabolism. Magnesium contributes to normal muscle and nerve function, supporting physical performance and relaxation. Selenium functions as an antioxidant and supports thyroid function. Iron is essential for oxygen transport in the blood and energy production. Potassium helps maintain normal blood pressure and electrolyte balance.
These minerals work synergistically to maintain optimal physiological function and overall well-being.
Antioxidants and Cellular Health
Antioxidants are compounds that help protect cells from oxidative stress caused by free radicals. These unstable molecules are produced naturally during metabolism and can accumulate from environmental factors. Antioxidants like vitamins C and E, selenium, and polyphenols work to neutralize free radicals, supporting cellular integrity and promoting long-term health. Regular consumption of antioxidant-rich foods—such as berries, leafy greens, nuts, and seeds—can contribute to general well-being.
Dietary Sources of Key Nutrients
A balanced diet provides most essential nutrients naturally. Here are key dietary sources:
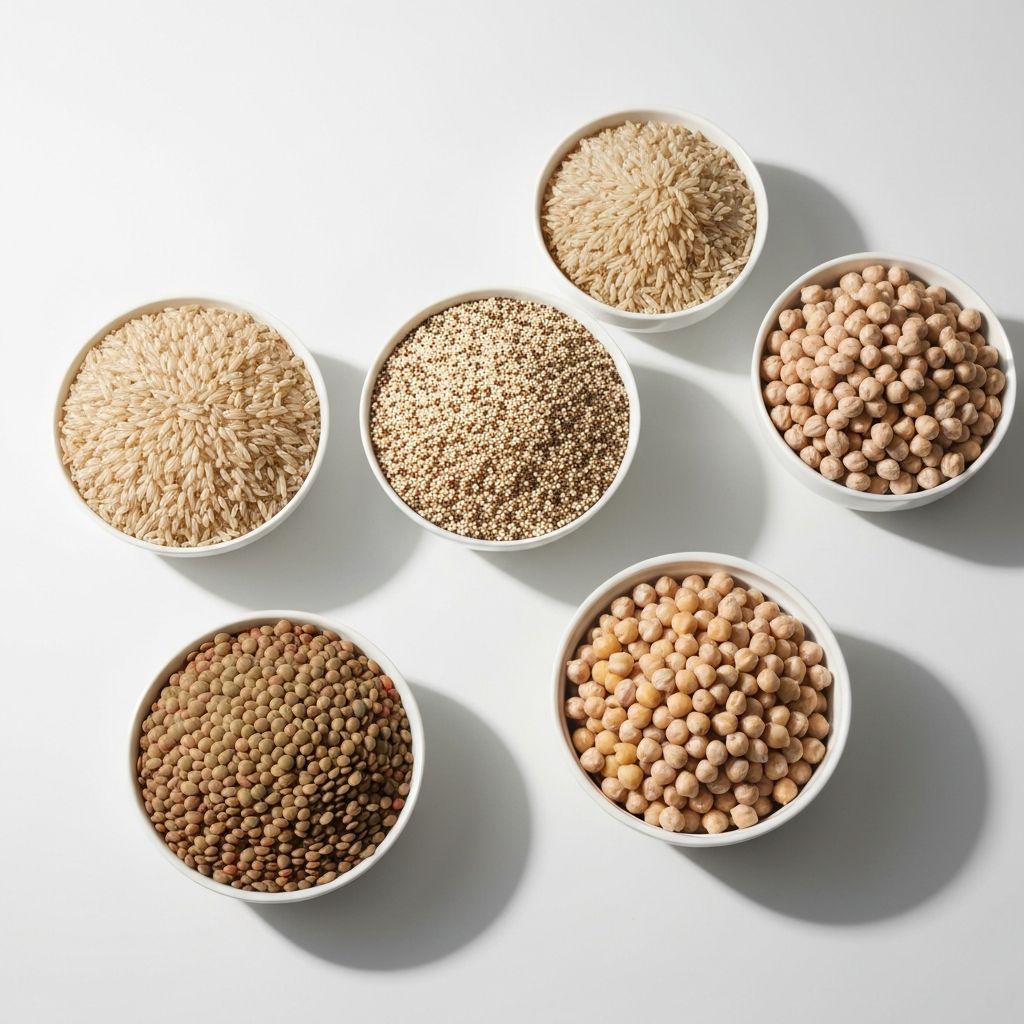

Whole Grains & Legumes
Brown rice, quinoa, oats, lentils, and chickpeas are excellent sources of B vitamins, fiber, magnesium, and iron. These foods support sustained energy and overall digestive health.
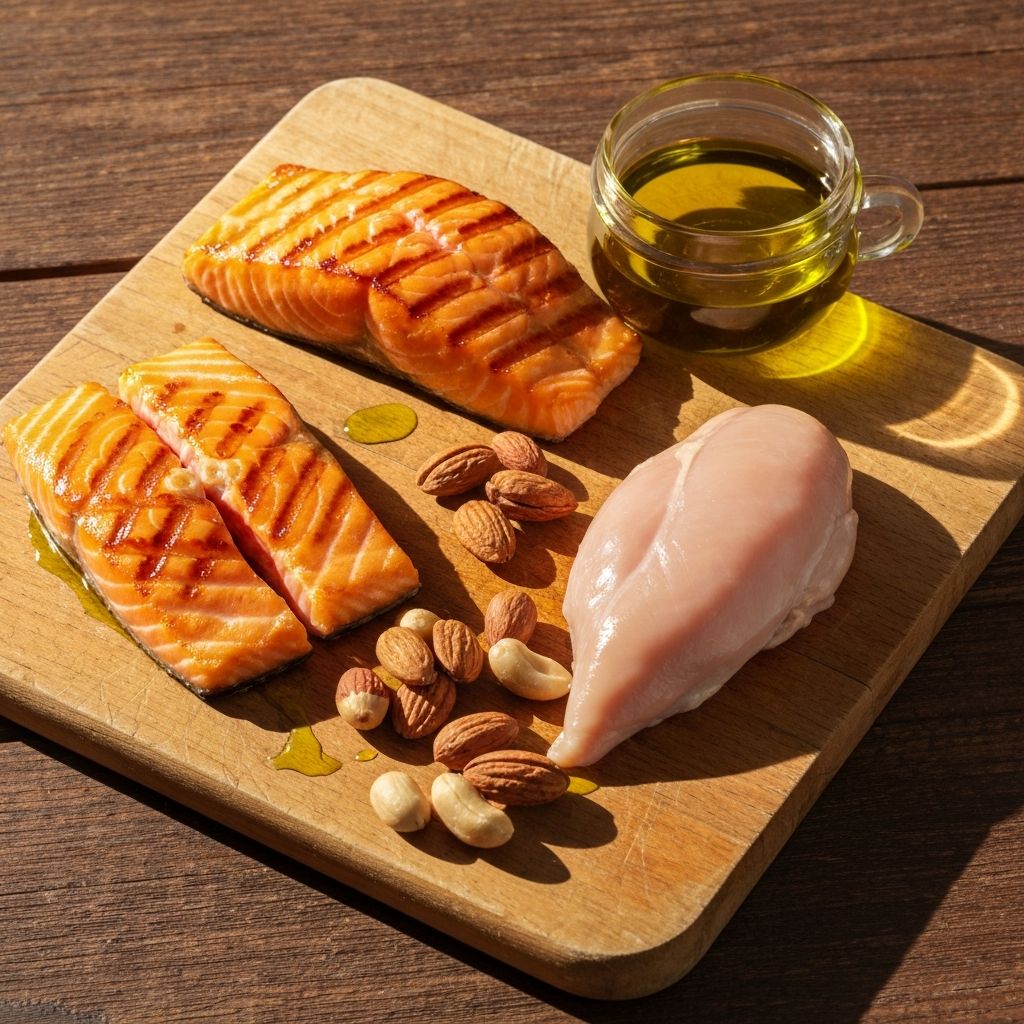

Lean Proteins & Healthy Fats
Salmon, chicken, turkey, nuts, and seeds provide protein, omega-3 fatty acids, zinc, and selenium. These foods support muscle function and cardiovascular well-being.
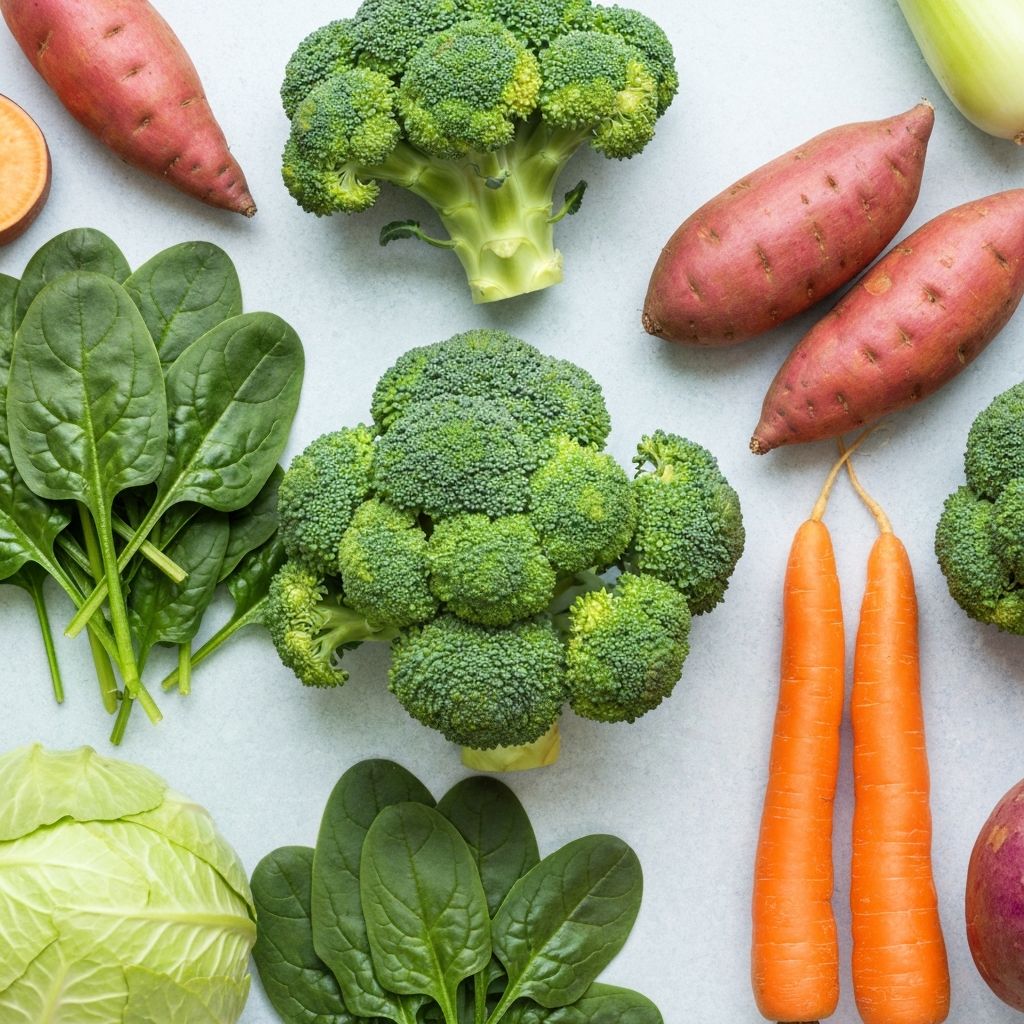

Fresh Vegetables & Fruits
Spinach, broccoli, sweet potatoes, berries, and citrus fruits deliver vitamins C, D, E, folate, and various minerals. These foods support immune function and antioxidant protection.
Lifestyle and Well-being
Nutrition works best when combined with a holistic approach to health. Regular physical activity—whether through walking, running, strength training, or yoga—enhances cardiovascular function and supports overall vitality. Adequate sleep is equally important, as it allows the body to repair and regenerate. Stress management through meditation, outdoor activities, or hobbies contributes to mental and physical well-being. When these lifestyle elements align with balanced nutrition, the cumulative effect promotes sustained energy, resilience, and quality of life.

The Science Behind Nutrient Absorption
Understanding how the body processes nutrients helps clarify why both diet quality and bioavailability matter. When you consume food or supplements, nutrients are broken down in the digestive system. The stomach and intestines absorb these compounds into the bloodstream, where they are transported throughout the body. Some nutrients are fat-soluble (A, D, E, K) and require dietary fat for optimal absorption, while others are water-soluble (B vitamins, C) and don't have this requirement. Factors like digestive health, nutrient combinations, and food form influence absorption efficiency.
Common Nutritional Misconceptions
Several myths persist about nutrition and supplements. Here are common misconceptions clarified:
- Myth: All supplements work the same. Fact: Quality, form, and bioavailability vary significantly between products. Third-party testing can verify content accuracy.
- Myth: More nutrients are always better. Fact: The body has specific requirements; excess amounts are often excreted and provide no additional benefit.
- Myth: Supplements replace a poor diet. Fact: Whole foods contain fiber, phytonutrients, and complex interactions that supplements cannot fully replicate.
- Myth: Natural products are always safe. Fact: Potency and safety vary; individual sensitivities and interactions with medications must be considered.
- Myth: Results appear quickly. Fact: Nutritional changes support cellular processes that typically require consistent effort over weeks or months.
Building a Balanced Diet
Creating a nutritionally complete eating plan doesn't require complexity. Focus on including a variety of nutrient-dense foods:
- Protein sources at each meal (legumes, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy) support muscle maintenance and metabolic function.
- Colorful vegetables and fruits provide vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber essential for digestive and cellular health.
- Whole grains instead of refined carbohydrates support sustained energy and provide B vitamins and minerals.
- Healthy fats (olive oil, nuts, avocados, fatty fish) support brain function and reduce inflammation.
- Hydration enables nutrient transport and supports all physiological processes.
- Portion awareness ensures adequate intake without excess caloric consumption.
Exploring Advanced Nutrients
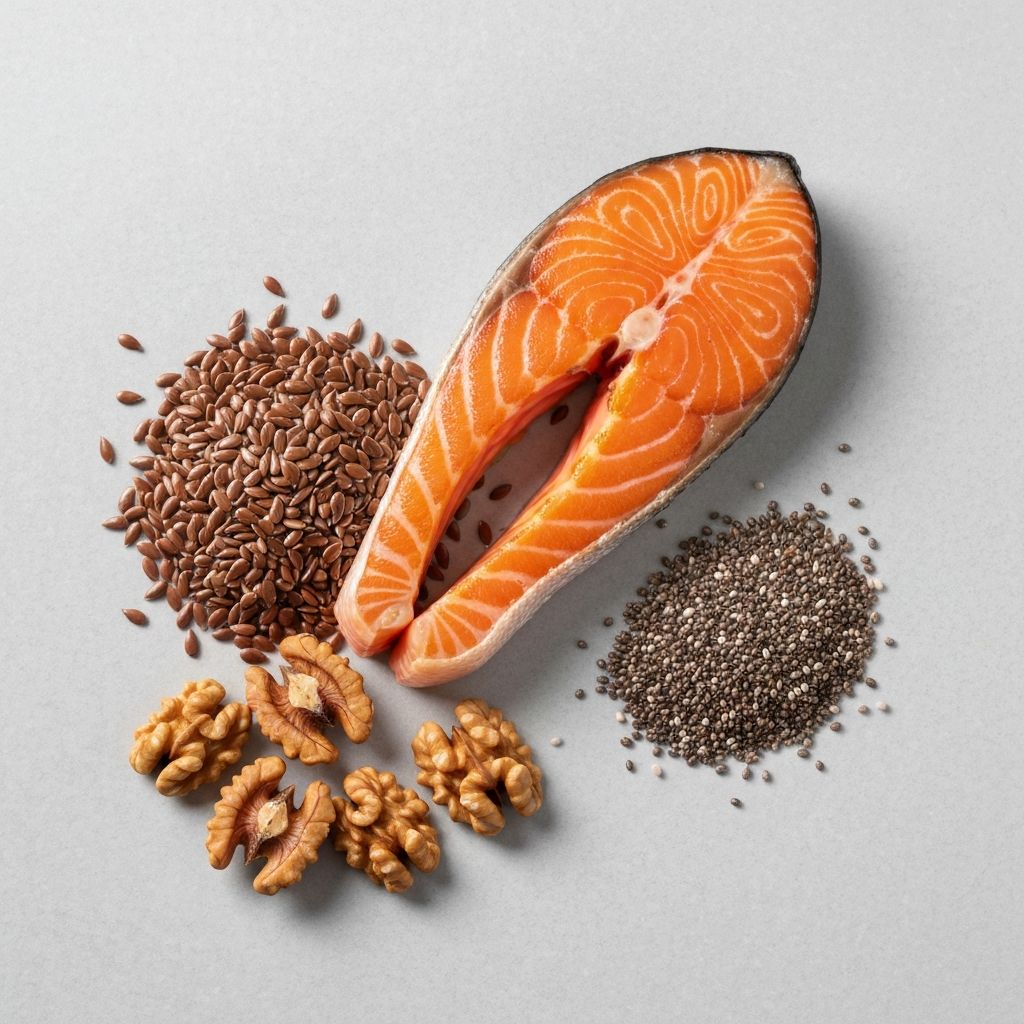
Omega-3 Fatty Acids (EPA and DHA) are polyunsaturated fats that support brain function, cardiovascular health, and normal inflammatory responses. Found primarily in fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, these compounds play roles in vision health, cognitive function, and overall cellular function.
CoQ10 (Coenzyme Q10) is a fat-soluble compound essential for cellular energy production. It functions as an antioxidant and plays a particularly important role in heart health, supporting normal cardiovascular function.
Alpha-Lipoic Acid is a potent antioxidant that supports metabolic processes and nerve health. It crosses the blood-brain barrier, providing neuroprotection and supporting neurological well-being.
These advanced nutrients complement a foundation of basic vitamins and minerals, offering additional support for specific health aspects.

Educational Disclaimer
This information is for educational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. It does not replace professional medical consultation, diagnosis, or treatment. Individual nutritional needs and responses vary. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional before making any decisions about your health or diet.
Educational content only. No promises of outcomes.
Get in Touch